Some Experiments into How Google's Crawler works
Why experiment with Googlebot Beyond the fact it is interesting to understand how it works, it is potential useful if you ca...
Expert insights, guides, and tips to improve your website's SEO performance
There you are, doing your daily ritual of checking the "Google Page Data" report in The Crawl Tool and you come across this:
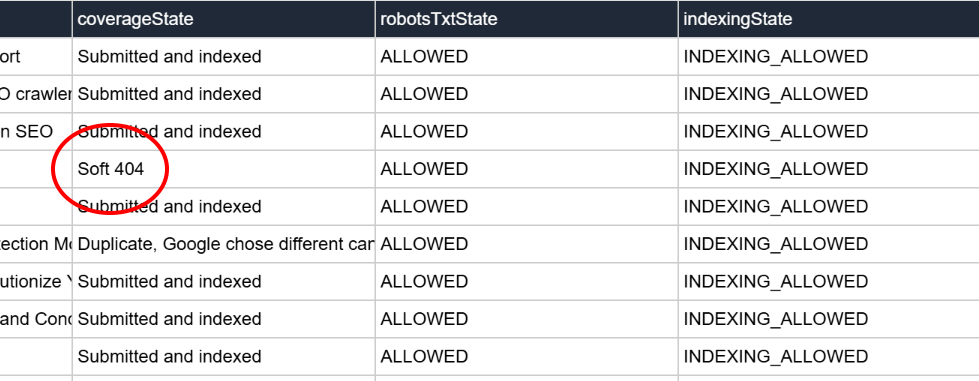
We all know that 404 means page not found, but what exactly is a Soft 404?
HTTP is the protocol behind serving web pages, it was later expanded to include HTTPS, but the differences in that expansion aren't important here. It has always been the case the a web server serves status codes with web pages in response to an https. Many of these you will know. 200 for "okay". 301 for a permanent redirect. 302 for a temporary redirect. 404 for page not found. This was originally so that web browsers could read the status and take the appropriate action or inform the user. Later, web crawlers like Google's used them to guide their crawls. After all, all of that is helpful for them to know.
The first instance I can find of talk about "Soft 404s" is in 2008. We should be clear here that a "Soft 404" isn't an official thing. It's not part of the standards that the internet is based upon. Google appears to have simply made it up.
As we've mentioned, when a requested page doesn't exist, the server is meant to return a 404 status code. In the old days of the internet often the browser would choose the text to display to the user. But nowadays it is way more common for websites to send a web page along with the 404 to inform the user, like with those funny messages that the website owner things are cute but aren't funny. The standards allow that, that text could technically be anything.
It is possible that a website is misconfigured. In that case it could return the content of a 404 page, but without the 404 status code. A visitor to such a website would highly likely not notice, because the status code isn't rendered anywhere so they are seeing exactly the same visual 404 page as they would otherwise see.
A web crawler, however, is dumb. It does not really "see" the web page and is therefore pretty reliant on the 404 status code being sent correctly. This is what the made up term "Soft 404" refers to - pages that are delivering a 404 alongside a page that basically says the page could not be found. It's relevant only to automated systems like Google.
Running a web crawler is actually expensive and everything you want to store in the search index is taking costly space. If servers are returning page not found errors but not the 404 codes then a crawler is crawling it and storing it as a search result, which is essentially useless from the search engine's perspective. It's as simple as that.
In years gone by, search engines used to compete by proudly announcing the number of web pages in their index. That's not really a metric that defines usefulness to the searcher. It is no more. That's a good shift as it encourages search engines to think more about their users, and ultimately these so called "Soft 404s" aren't useful.
Observationally though, in recent years with the advancement of AI Google has become more aggressive at pruning what pages it wants to crawl. We can guess they want to use resources used for crawling for AI instead. Efforts to ramp up crawler efficiency therefore seem to be in progress.
Detecting a so called "Soft 404" is not an easy thing to do, it also has a cpu usage cost associated of doing the actual check. There's a catch 22 in there - if you try to too accurately detect such pages then you end up spending more resources than gain by being able to filter them out. Any balanced level will always have a lot of false positives - pages that aren't so called Soft 404s that are detected as such. If you're a search engine with a lot of pages in your database, you can afford that. In fact, if you're trying to save costs you can make it really aggressively filter and accept lots of false positives because you probably already cover the topic those pages were about. Good for search engines, not so great for the website owners.
Okay, so one of you're pages has been hit by Google's made up term and aggressive cost cutting and a genuine page of yours is marked as a soft 404. What are your options? Well, the answer is kind of easy. Think about how you would set up a 404 page. It tends to have a standard template and very little text, perhaps a heading and a sentence or two.
Now do the opposite. Add some paragraphs of text in. Now it doesn't look like a 404 page! That was easy. Given it has been marked as a kind of 404, it may take Google's crawler some time to come back and read and update it. With Google being ever stricter on crawl budget allocations for the same reasons mentioned above, it could take some time. Patience is key. Or just give it a new url because crawlers are stupid, a new url is a new page according to a crawler.
Start with a free crawl of up to 1,000 URLs and get actionable insights today.
Try The Crawl Tool Free
Why experiment with Googlebot Beyond the fact it is interesting to understand how it works, it is potential useful if you ca...

LLMS.TXT again I've written about LLMS.TXT in the article about how getting one listed in an llms.txt directory mysteriously...

What's this about Adding Other Media to robots.txt I recently came across John Mueller's (a Google Search advocate) blog. I ...

Understanding the Importance of having a fast Mobile website I, personally, spend a lot of time focusing on site speed. The ...
What are robots.txt, sitemap.xml, and llms.txt These files are used by search engines and bots to discover content and to le...

AI Crawlers and Citing Sources The rise of AI, rather than search, crawlers visiting websites and "indexing" information is ...